
Before you use a particular function, review that function's syntax. One of the arguments is usually an identifier or an expression. įunctions The general form is: Function(argument, argument) It is not uncommon for an identifier to take the form. You only have to specify enough parts of an identifier to make it unique in the context of your expression. You can also use an expression as part of another expression - typically as an argument of a function. Any valid expression must contain at least one function or at least one identifier, and can also contain constants or operators. To build an expression, you combine identifiers by using functions, operators, constants, and values. You can also use expressions in the Validation Rule property for a table field. For example, you can use expressions in the Control Source and Default Value properties for a control.
Tables, queries, forms, reports, and macros all have properties that accept an expression. Expressions are used in many places to perform calculations, manipulate characters, or test data. You can use this expression in the Validation Rule property of a control or table field to ensure that only positive values are entered. True when it is compared to a number that is greater than 0.įalse when it is compared to a number that is less than 0. For example, this Boolean expression consists of just an operator and a constant: >0 This expression can be used in a text box in a form footer or report footer to calculate sales tax for a group of items.Įxpressions can be much more complex or much simpler than this example. The nesting limit for expressions in a web database is 65Īn expression is a combination of some or all of the following: built-in or user-defined functions, identifiers, operators, values, and constants that evaluate to a single value.įor example, the following expression contains common components: =Sum()*0.08 In this articleįunctions, operators, constants, and values But with a good understanding of expression syntax and a little practice, it becomes much easier. Initially, expressions in Access are a little bit hard to read. Syntax is the set of rules by which the words and symbols in an expression are correctly combined. To use expressions, you write them by using proper syntax. You can calculate these values by using expressions.
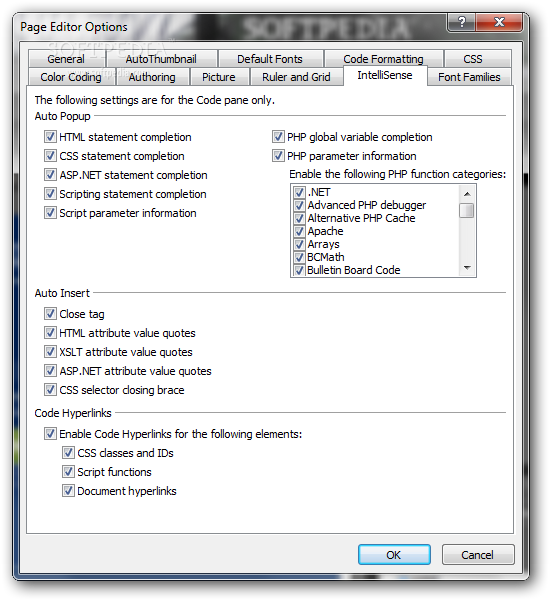
For example, you want to calculate sales tax on an order, or calculate the total value of the order itself. When you use Microsoft Access, you often need to work with values that are not directly in your data.
Access for Microsoft 365 Access 2021 Access 2019 Access 2016 Access 2013 Access 2010 Access 2007 More.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
